What is Forex?
By:
Emma Harris
On
26/07/2024Reading time:
5 min
Summary:
Forex trading is a dynamic and complex activity that offers numerous opportunities for profit. By understanding the basics and familiarizing yourself with standard forex terms and abbreviations, you can navigate the forex market more effectively. Remember, successful trading also involves diligent risk management and staying informed about market conditions.

A Beginner's Guide to Forex Trading
Forex, or foreign exchange, refers to the global marketplace where currencies are traded. This market is crucial for international trade and finance, allowing businesses, governments, and individuals to convert one currency into another. The forex market is the world's largest and most liquid financial market, with daily trading volumes exceeding $6 trillion.
Why Trade Forex?
Liquidity: With high trading volumes, positions can be entered and exited quickly without significantly affecting the price.
24-Hour Market: The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing for trading at almost any time.
Leverage: Forex brokers often provide leverage, allowing traders to control more prominent positions with relatively little capital.
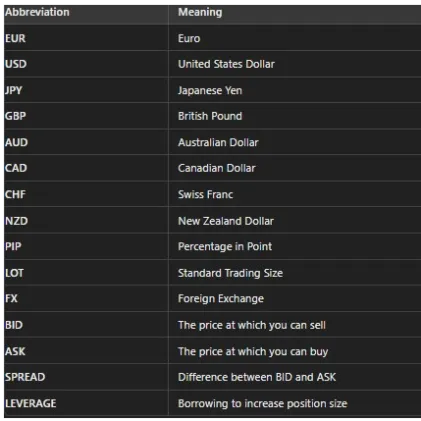
Discommon Forex Abbreviations Explained

How Forex Works
In the forex market, currencies are traded in pairs. Each pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency. The base currency is listed first, while the quote currency is the second. The exchange rate tells you how much of the quoted currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.
For example, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro (EUR) is the base currency, and the U.S. dollar (USD) is the quote currency. If the exchange rate for EUR/USD is 1.20, 1 euro is equivalent to 1.20 U.S. dollars.
Who Trades in the Forex Market?
Banks: Major players that trade large volumes of currency on behalf of clients and for their accounts.
Corporations: Businesses involved in international trade that need to exchange currencies.
Governments and Central Banks: They intervene in the forex market to control inflation, stabilize their currency, and manage economic growth.
Retail Traders: Individual traders who participate in the market through online brokers.
